7. Diurnal cycle of convection¶
7.1. Overview¶
The diurnal cycle of precipitation and radiative fluxes is closely related to the representation of boundary-layer turbulence and cumulus clouds, as well as to the triggering criteria of the deep convection scheme, which will give the onset of precipitation, and its closure, which in turn determines its intensity and duration. Associated clouds will have a different radiative impact given their timing of occurrence within the day. Thus, the evaluation of the representation of the diurnal cycle of precipitation and radiative fluxes gives interesting insights into the progress achieved in the design and setup of physical parameterizations.
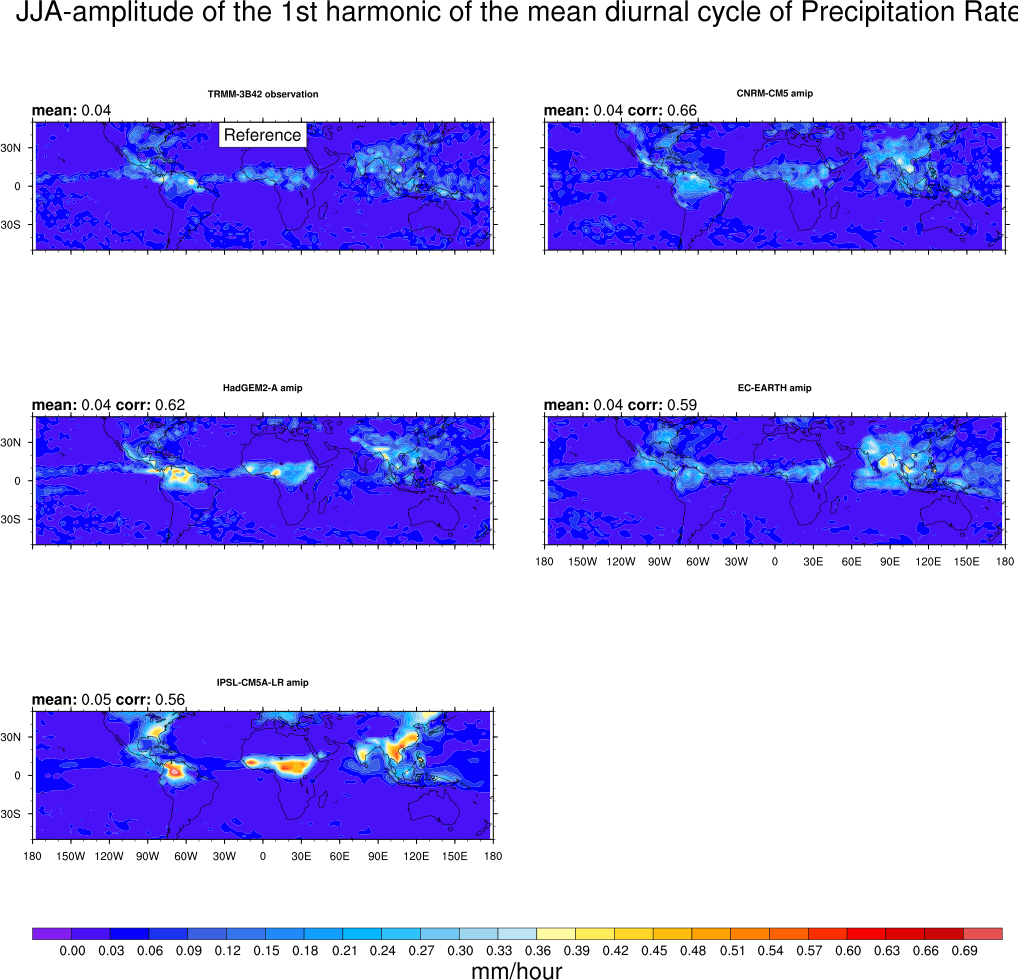
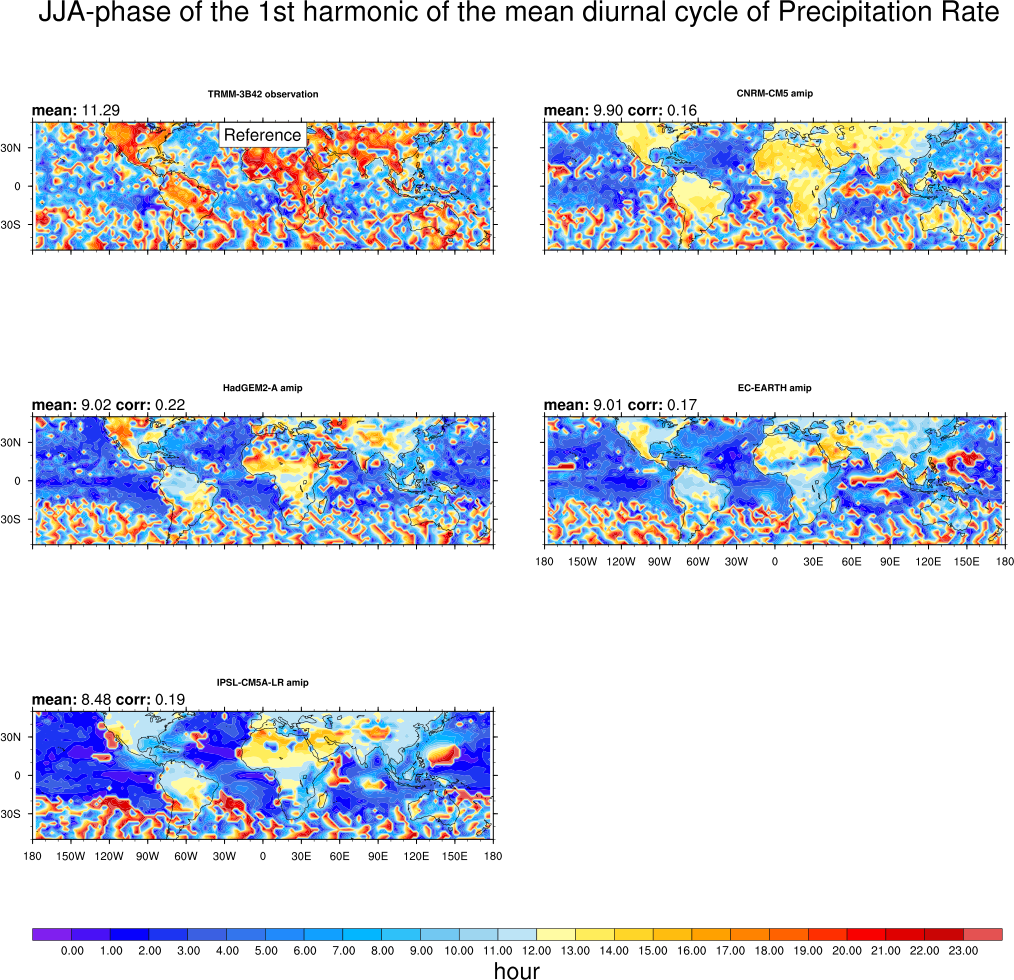
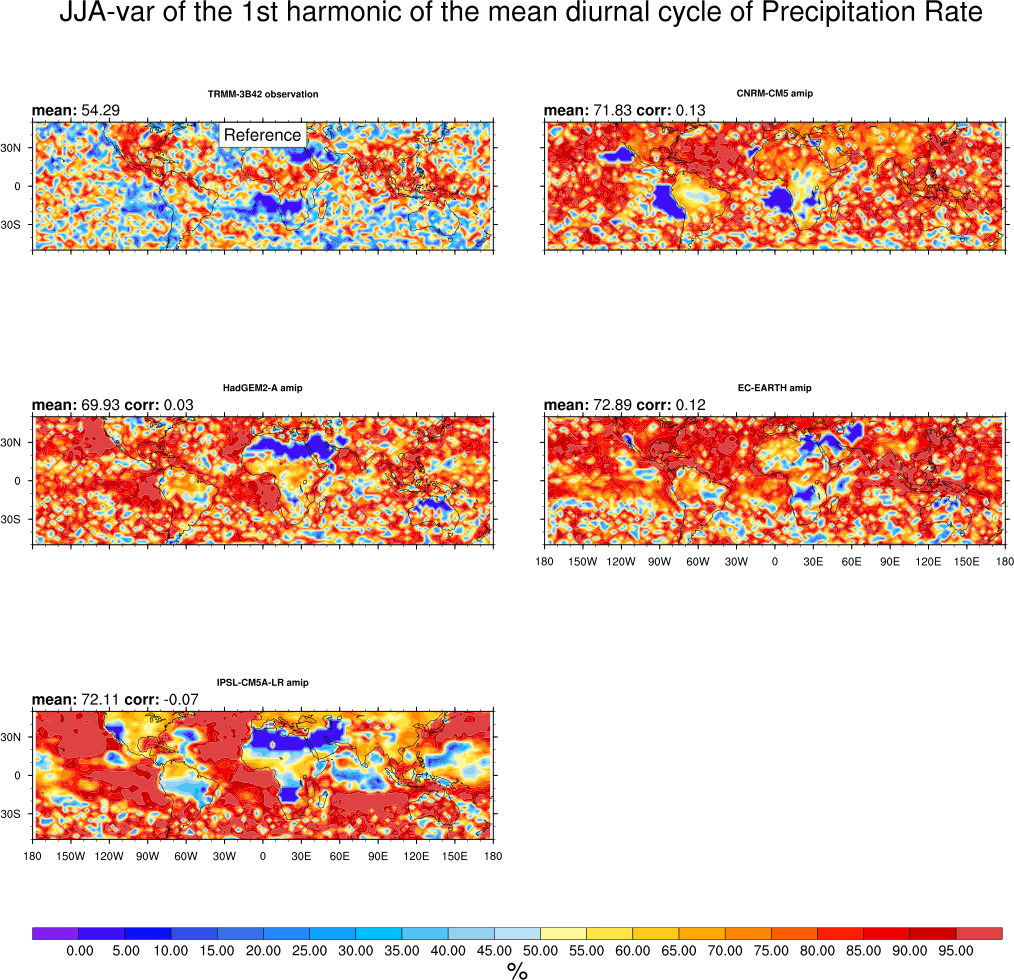
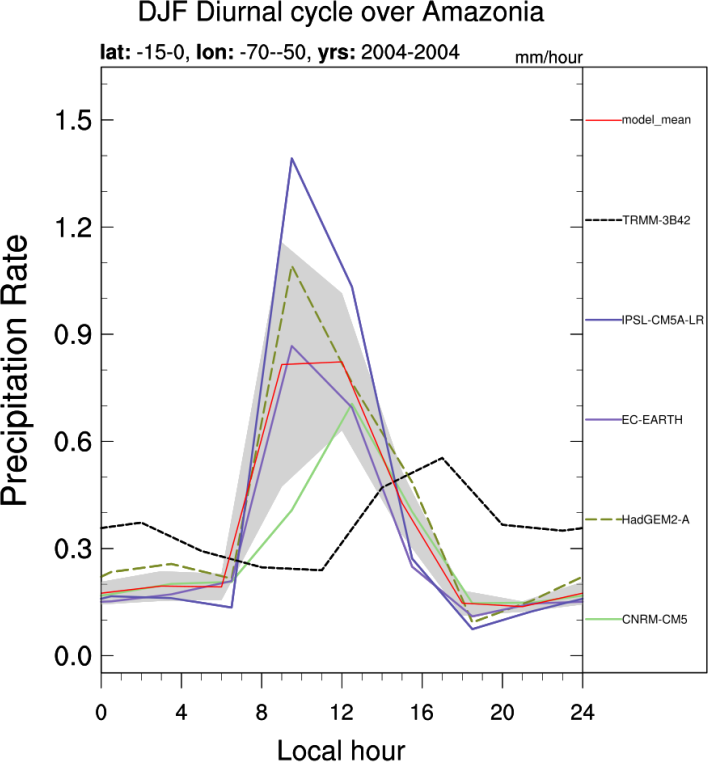
This diagnostic evaluates the representation of the diurnal cycle of precipitation over specific regions in the Tropics. The diurnal cycle is known to be different over land and ocean. Over land, the semi-arid Sahel region is contrasted with humid regions (Amazonia) as well as with the two monsoon regions West-Africa and India. Over the ocean, the diagnostic focuses on the Gulf of Guinea, the Indian Ocean and the East and West Equatorial Pacific. A harmonic analysis is done to provide global maps of the timing and amplitude of maximum rainfall with 3-hourly TRMM observations used as a reference.
Optionally, the analysis can be extended to include the diurnal cycle of radiative fluxes at the top of the atmosphere and at the surface (LW and SW, total and clear-sky components). 3-hourly CERES data are used as a reference derived from measurements at the top of the atmosphere and computed using a radiative transfer model at the surface.
7.2. Available namelists and diagnostics¶
Namelists are stored in nml/
- namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_pr.xml
- namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_SFCflux.xml
- namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_TOAflux.xml
- namelist_DiurnalCycle_harmonic.xml
Diagnostics are stored in diag_scripts/
The following diagnostic script is called by namelist_DiurnalCycle_harmonic.xml:
- DiurnalCycle_precip_harmonic.ncl: computes the amplitude, phase and percentage of the variance of the first harmonic of the mean diurnal cycle of precipitation by season over the globe. 3-hr mean precipitation outputs are used and interpolated onto a common 2.5°x2.5° grid.
The following diagnostic script is called by namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_pr.xml, namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_SFCflux.xml, namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_TOAflux.xml:
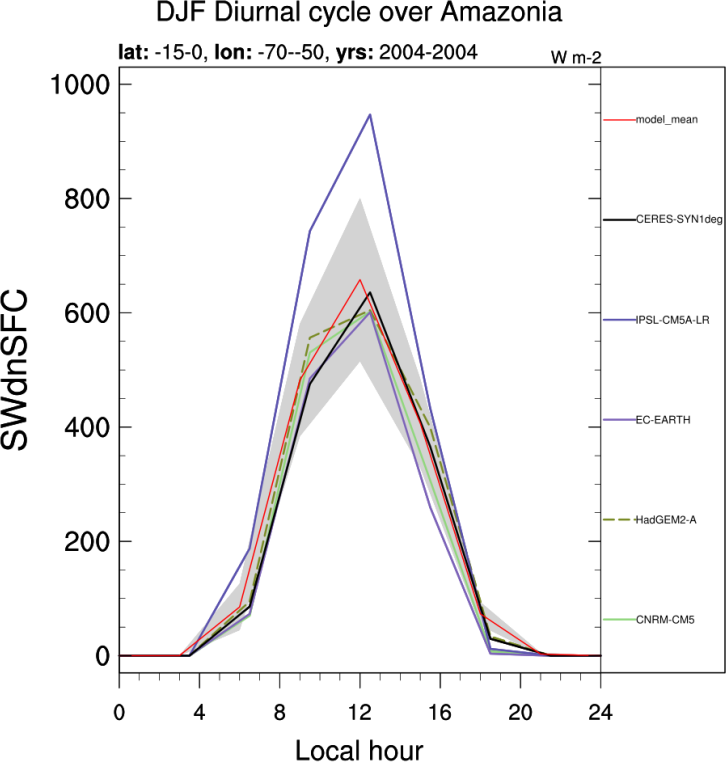
- DiurnalCycle_box.ncl: computes the mean diurnal cycle of precipitation and available radiative fluxes over specific regions and seasons. Regions include Sahel (Sahel, 12°N-23°N, 10°E-10°W), West-Africa (WestAf, 4°N-10°N, 8°E-8°W), Gulf of Guinea (GoG, 2°S-4°N, 8°E-8W), Amazonia (Amazon, 15°S-0°, 70°W-50°W), India (India, 12°N-20°N, 75°E-80°E), Indian Ocean (IO, 10°S-5°N, 70°E-90°E), East-Equatorial Pacific (EEP, 0°-10°N, 110°W-90°W) and West-Equatorial Pacific (WEP, 0°-20°N, 130°E-150°E). Seasons include DJF, MAM, JJA and SON.
7.3. User settings¶
User setting files (cfg files) are stored in nml/cfg_DiurnalCycle/
- namelist_DiurnalCycle_harmonic.xml
Required diag_script_info attributes
- season: season (DJF, MAM, JJA, SON)
- destgrid: common grid for interpolation (“2.5x2.5”)
- latrange_basic: latitude range of box
- lonrange_basic: longitude range of box
- cn_levels_amplitude_basic: contour levels for amplitude plots
- cn_levels_phase_basic: contour levels for phase plots
- cn_levels_var_basic: contour levels for percentage of variance
- styleset: “CMIP5”, “DEFAULT”
- my_region: label for region
- namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_pr.xml, namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_SFCflux.xml, namelist_DiurnalCycle_box_TOAflux.xml
Required diag_script_info attributes
- season: season (DJF, MAM, JJA, SON)
- latrange: latitude range of box
- lonrange: longitude range of box
- styleset: “CMIP5”, “DEFAULT”
- box: label for region
- multi_model_mean: calculate multi-model mean (“y”, “n”)
- supporting_gridlines: display supporting gridline (“y”, “n”)
- x_gridlines: display gridline along x-axis (“y”, “n”)
- y_gridlines: display gridline along y-axis (“y”, “n”)
7.4. Variables¶
- pr (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rsds (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rsdscs (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rlds (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rldscs (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rsus (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rsuscs (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rlus (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rlut (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rlutcs (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rsut (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
- rsutcs (atmos, 3hr mean, longitude latitude time)
7.5. Observations and reformat scripts¶
Note: (1) obs4mips data can be used directly without any preprocessing; (2) see headers of reformat scripts for non-obs4mips data for download instructions.
- TRMM-3B42, 3-hr, 0.25°x0.25°: pr (obs4mips)
- CERES-SYN1deg, 3-hr, 1°x1°: rsds, rsdscs, rlds, rldscs, rsus, rsuscs, rlus, rsut, rsutcs, rlut, rlutcs
Reformat scripts: reformat_scripts/obs/reformat_obs_CERES-SYN1deg-SFC.bash, reformat_scripts/obs/reformat_obs_CERES-SYN1deg-TOA.bash
7.6. References¶
None.